022 2540 4455
96536 65448
Reproductive Medicine/ Infertility
1. Couple fertility test
Fertility tests are the best way to know about your infertility status and can help you find the cause of it.
If under the age of 35 years and trying regularly for 12 months.
If above the age of 35 years and trying regularly for 6 months.
One should seek help before the above duration, if one has
- Thyroid problems
- PCOS
- Erectile or ejaculatory dysfunction
- Irregular periods
- Repeated Miscarriage
- Past Ovarian/Uterine surgery
- Family history of early menopause
In males, Semen Analysis is most common test performed.
The male partner is asked to give semen sample which will be assessed by andrologist for volume, count, motility, morphology and other parameters. Other tests like sperm DNA fragmentation and others can be done as per history.
In females, after a detailed history, Pelvic Ultrasound is performed to asses the uterus and ovaries.
Uterus is assessed for the endometrial lining, blood flow and any other abnormalities.
Ovaries are assessed for the follicle count which gives an estimate of the ovarian reserve .
Certain blood tests may be advised to find out any hormonal problems.
After that, the couple is explained about normal fertility and advice given based on the reports.
Remember that your doctor will plan tests based on you and your partner situation and medical history. Thus, you and your partner may not require all of the tests, and they may be done in a different order depending from doctor to doctor.
2. Evaluation Of Male Partner
- In 50 % of cases, male factor is responsible for infertility. Hence a good semen analysis from a trained Andrologist is a must.
- Along with it, thorough history and genitalia examination throw light on erectile, ejaculatory and other problems like varicocele etc
- Certain specialized tests like Sperm Function Test, DNA fragmentation rate and Mitochondrial assay are done in specialized circumstances so as to enhance the result.
- Sperm function test gives an idea of the capacity of sperm to fertilise an egg.
- DNA fragmentation rate gives an idea of genetically normal sperms. High fragmentation rate is associated with higher rates of abortion.
- The male partner is asked to provide a semen sample
- For a good semen analysis, one should abstain from sexual intercourse for 2-3 days. Lesser or greater abstinence may affect the report
- Intake of alcohol, caffeine or any sort of medications should be avoided for 2-5 days
- No lubricant should be used as it affects the motility
- Ideally the sample should be collected in a sterile, wide-mouth, labeled, tissue culture graded container within the hospital premises. However if collected at home, it should reach the hospital within 30 mins and should be maintained at body temperature
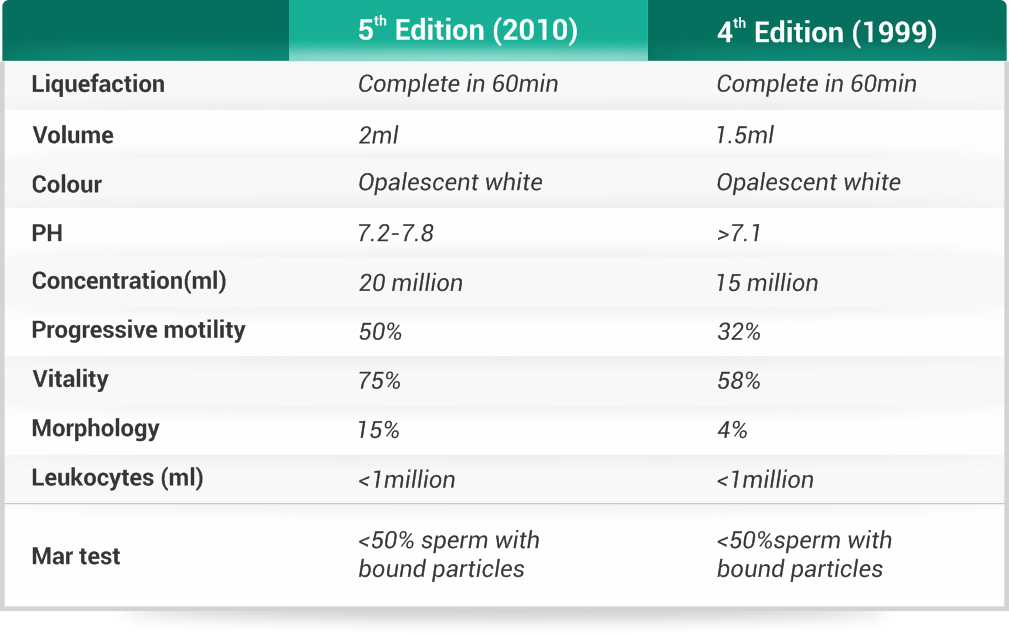
- Liquefaction: After the ejaculation, the semen sample is coagulated and needs to be liquefied in order to perform any tests. In normal conditions the semen is totally liquefied within 60 minutes after the ejaculation.
- Viscosity: When the semen sample is very viscous it may be a sign of a prostatic dysfunction.
- Volume: The normal volume of an ejaculate sample after 3 or 5 days of sexual abstinence is approximately 1.5 ml. Lower volumes suggests hypospermia.
- Colour: Semen is usually opalescent white, lightly yellow. When the colour is altered, it is recommended to study possible causes.
- pH: Values should be greater than 7.1. Lower values might be a sign of azoospermia (lack of spermatozoa) or chronic inflammatory processes.
- Sperm concentration: Normal values are around 15 million per ml ejaculated or 39 million per complete semen sample. When these values are lower it indicates Oligozoospermia.
- Motility: The percentage of motile spermatozoa and progressively motile is analyzed. The progressive motility value should be over 32%. If less it indicates Astenozoospermia.
- Vitality: The percentage of vital spermatozoa must be over 58%. Lower values indicate Astenoozoospermia.
- Morphology: Atleast 4% or more sperms should be normal in morphology. Lower percentage indicates Teratozoospermia.
- Leukocytes: When the leukocyte concentration is over 1 million per ml of sample it might indicate an infection (leukocytosis).
3. Evaluation Of Female Partner
- Detailed menstrual, medical, surgical and sexual history is taken
- After a detailed history, pelvic ultrasound is performed to asses the uterus and ovaries. Ultrasonography mainly transvaginal can help in detecting the cause behind infertility in some cases
- Uterus is assessed for the size, endometrial lining, blood flow and any other abnormalities like Abnormal uterine shapes (Septate uterus, bicornuate uterus), Fibroid uterus, Endometrial polyp, Calcifications, Adhesions or Ashermann syndrome
- Ovaries are assessed for the volume and follicle count which gives an estimate of the ovarian reserve or to detect any other abnormalities like Polycystic ovaries, Ovarian cyst (Endometrioma, Dermoid cyst, Simple cyst, corpus luteal cyst etc), Poor ovarian reserve, ovaries stuck to uterus as in PID
- Abnormal tubal pathology like Hydrosalpinx (fluid filled in the tube), Pyosalpinx (pus filled in the tube) ,Ectopic pregnancy can also be diagnosed with TVS
- Certain blood tests may be advised to find out any hormonal problems
- Follicular study is done in a fertility clinic
- It is better done transvaginally then trans abdominally
- It can be done in a natural as well as a stimulated cycle
- It is ideally started from D2 when the women is menstruating to assess the AFC(Antral Follicle Count)
- Then it is repeated on D8/9 and then every alternate day to monitor the growth of follicle (Egg in the ovary) and its rupture (Ovulation) and also the endometrial lining in response to follicle
- One of the important tests to asses ovarian reserve is serum AMH i.e. Anti-Mullerian Hormone and AFC
- After that, the couple is explained about normal fertility and advice given based on the reports
- AMH that is Anti-Mullerian hormone is a hormone secreted by granulosa cells of pre-antral and antral follicles of the ovary. It gives an estimate of ovarian reserve (that is no of eggs remaining) which determines fertility
- It is blood tests which can be performed on any day of menstrual cycle
- They decrease with increasing age of the women
- If AMH count is good, it indicates good fertility status
- A women is born with fixed no of eggs for her lifetime which only reduce with age. Hence it is important to complete the family in time before the reproductive potential of women diminishes
- AMH levels and fertility potential
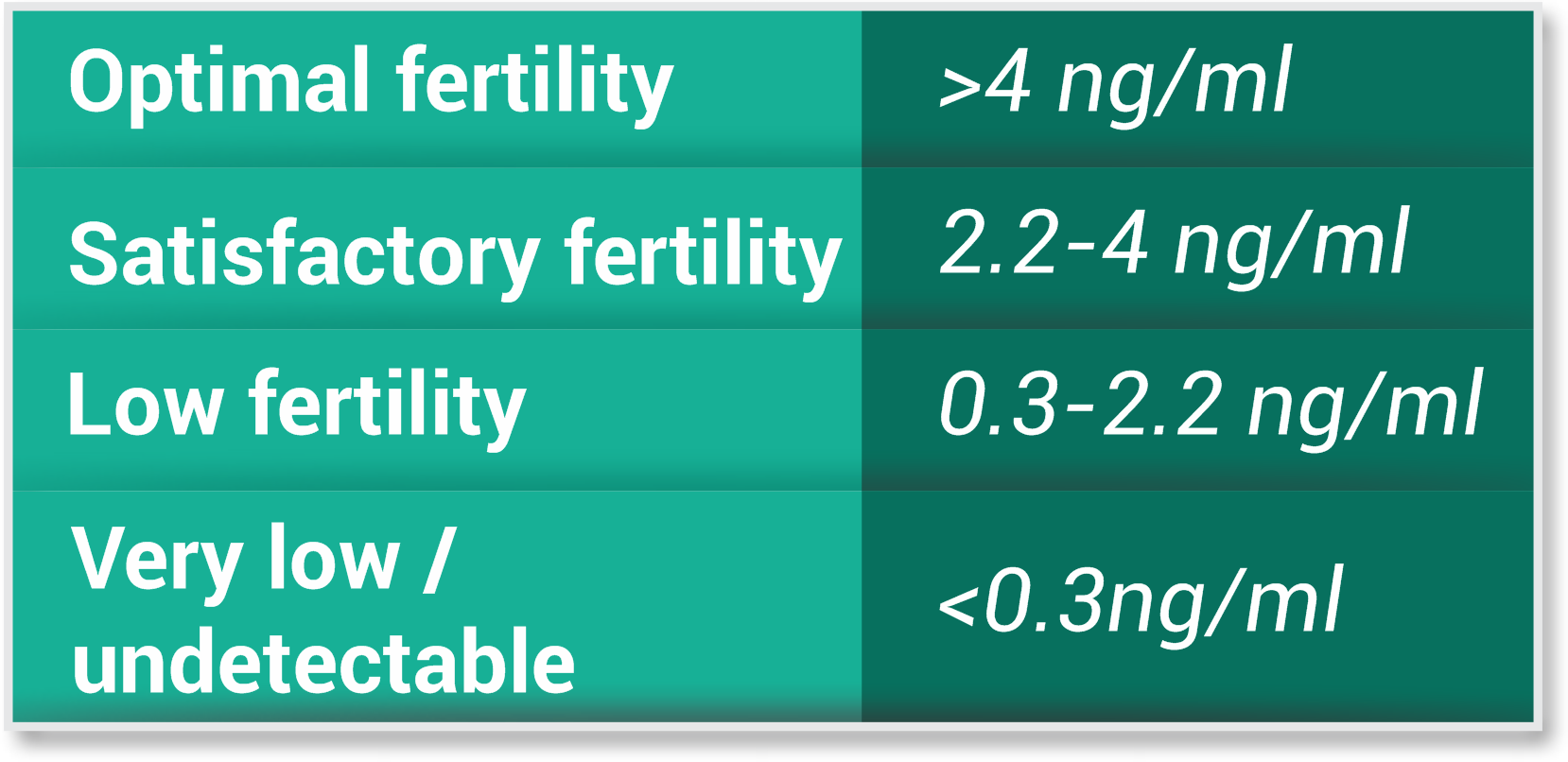
- It is important to remember that AMH levels decline and FSH levels increase as women ages. In other words, normal AMH and FSH levels change depending on a woman’s age.Because of this, focusing on age-specific AMH and FSH levels allows us to best assess a woman’s ovarian reserve, devise an appropriate treatment plan and estimate her IVF pregnancy chances.
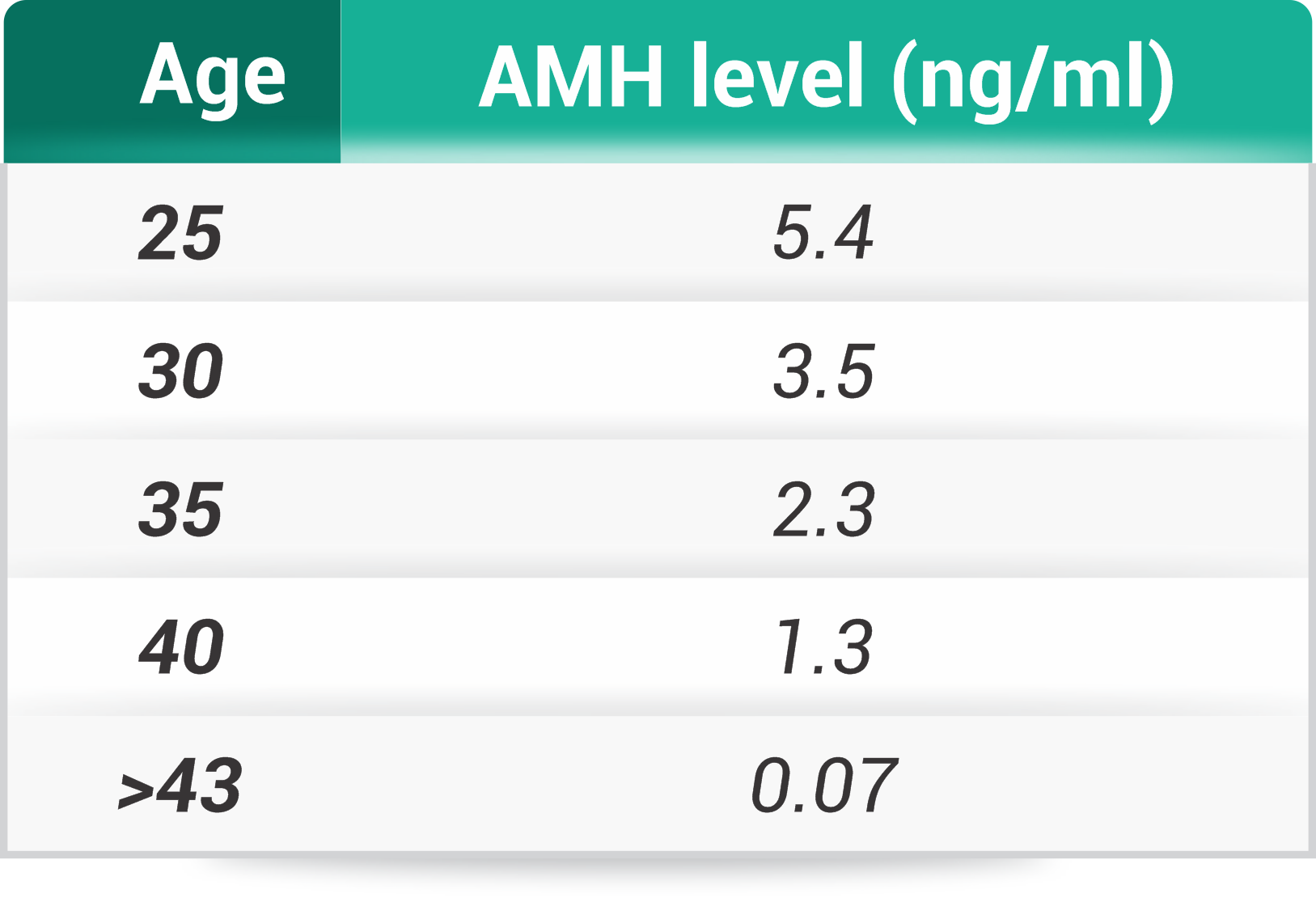
AFC is Antral follicle count.
- It is assessed by transvaginal ultrasonography on second or third day of your periods
- It gives an estimate of the follicles that can be recruited in that menstrual cycle
- Normal AFC should be 3-8 follicles less than 10mm in each ovary
- Total AFC less than 5 indicates poor ovarian reserve
- AFC of 5-15 indicate normal reserve
- AFC of more than 15 indicates polycytic ovaries
4. Sonosalphingography
- Sonosalpingography (SSG) is a diagnostic procedure used to test tubal patency
- Firstly foleys catheter is placed in uterine cavity
- Then 50-100 ml of normal saline is injected and flow of saline is visualised on ultasonography
- Patency is confirmed by observing a shower at the fimbrial end
- It can also be used to delineate submucous fibroid and detect intauterine lesions
5. Semen Wash And Intra Uterine Insemination (IUI)
- Intra-uterine insemination (IUI) also known as Artificial Insemination is a process in which the washed/processed semen is placed into the uterine cavity with the help of a catheter in and around the time of ovulation (release of egg from the ovary)
- The purpose of IUI treatment is to introduce the best and the most motile sperms high up in the uterine cavity i.e. as close to the ovum as possible so that the sperms have to travel the least distance
- It also overcome factors like cervical mucus opposition for its entry into the uterine cavity
- It is always done with follicular monitoring, the egg is matured and released or about to be released, which ensures that both the egg and sperm are timed properly for optimum fertilization and increased chances of pregnancy
- IUI treatment should always be done after confirming tubal patency
- The egg is usually alive for 24-48 hrs. after ovulation. Sperms are alive for around 48-72 hrs after they are released into the female genital tract. Thus, if processed / washed semen sample is deposited around this time, the chances of conception are very high
The success rate of IUI is averagely 12-15% but it depends on a several factors like women’s age, ovarian reserve, cause of infertility, duration of infertility, previous obstetric history, semen parameters and most importantly on stimulation protocol used.
Natural cycle IUI - 8-10%
Ovulation Induction with tablets and IUI-12-15%
Ovulation Induction with Injections and IUI-18-20%
Addition of GnRh antagonist increases the pregnancy rates further by 26-30%
Also more the no of pre-ovulatory follicles with good blood flow , better is the result.
- Mild to moderate male factor infertility- low sperm count, low motility
- Unexplained infertility (No apparent cause found for inability to conceive on routine recommended medical testing)
- Sexual or ejaculatory dysfunction
- Retrograde ejaculation
- Increased semen viscosity
- Time constraint (Husband working abroad )
- Cervical factor
- Minimal endometriosis
In a young couple (age
<35 yrs), 6 cycles of IUI Procedure with ovulation induction are advised whereas in an elderly couple (age>35 yrs) 3 cycles of IUI are advised.
However with other factors like Endometriosis , it is advisable to restrict to 3 cycles.
Cycles when done consecutively, that is back to back have better success rates.
It is important to individualise each case.
In cases of Azoospermia (No sperm count) or with severe male factor infertility, IUI is done with donor semen sample. The donor blood group and physical characteristics are matched.
Donor sample is procured from registered semen bank where donors are screened for viral infections.
- It is started from Day 2 or 3 of menses. Ultrasound is done to rule out cyst and determine AFC
- Patient is started on tablets or injections for ovulation induction
- Serial monitoring of follicle growth is done on Ultrasonography from Day 8 or 9 of menses
- When a good dominant follicle of more than 18mm with good peripheral vascularity is formed, Injection is given for rupture of follicle
- 36 hrs after injection, IUI is done
- Luteal support is given with medications
- After 14 days, patient is called for follow up for the results
Normally during intercourse the semen that gets deposited in the vagina contains seminal fluid (which helps to keep the sperms alive even in the acidic environment of the vagina) along with sperms. The cervix then acts as a barrier to this seminal fluid and allows only the motile sperms to enter into the uterus. The fluid that comes out after intercourse is the seminal fluid.
Only processed semen sample is used during IUI treatment. Processing helps to separate the active motile sperms from the seminal fluid and also from dead sperms, cellular debris, mucus, bacteria. This seminal fluid can be irritating to the uterine lining as it contains chemicals called Prostaglandins. Thus when the semen (unprocessed) is inserted directly into uterus, it could cause severe pain and cramping.
There are different techniques available for sperm processing:
Swim –Up Wash
Density Gradient Wash
Simple Wash
- It is an OPD procedure and doesn’t require admission
- It is one of the first line treatment which is completely safe
- It is usually painless but in cases of severe discomfort, sometimes it can be done under anaesthesia.
- In cases of difficult IUI, IUI must be done under ultrasonography guidance with help of traction with allis. One may consider cervical dilatation or Hysteroscopy for the same
- Usually only one IUI is done per cycle but in certain conditions like repeated failures and male factor infertility, two IUI give better result
- IUI can be done using Frozen husband sample, when husband is outdoor for long durations
6. IVF / ICSI- Test tube baby treatment.
IVF stands for In-vitro fertilization. It refers to the process by which a woman’s eggs are collected and then fertilized with sperms outside her womb in the laboratory.
Washed sperms are added in the petridish where eggs are collected so that one of the sperm fertilizes the egg.
The fertilized eggs (embryos) are then cultured in the laboratory and after appropriate growth; they are transferred back to the uterine cavity.
It thus bypasses the fallopian tubes completely.
ISCI stands for Intra Cytoplasmic Sperm Injection in which sperm is injected into the oocyte instead of placing them together and allowing them to fertilize naturally. ICSI is thus a very effective method to get fertilization of eggs.
It is done by trained embryologist using specialized micro-manipulation tools and equipment and inverted microscopes which help them to select the most morphologically normal and active sperm to be injected into the oocyte cytoplasm.
This usually results in normal fertilization in approximately 70-85% of eggs injected with viable sperm.
- Women with tubal diseases like blocked tubes, hydrosalpinx, and previous tubectomy done
- Patent tubes but non-functional like in previous pelvic inflammatory disease or tubal tuberculosis
- Infertility due to endometriosis
- Unexplained infertility
- Infertility due to male factors like oligospermia (low count), asthenozoospermia (less motility), teratozoospermia (abnormal sperms) or a combination of abnormalities like oligoasthenoteratozoospermia
- Previously failed IVF cycle due to failed fertilization
- Severe male factor Infertility- Oligoasthenoteratozoopermia- that is very low count, low motility or high percentage of abnormal sperms
- Sperms obtained through TESA (Trans Epididymal Sperm Aspiration), PESA (Percutaneous Epididymal Sperm Aspiration ), TESE (Trans Epididymal Sperm Aspiration) or Testicular Biopsy-sperms are obtained microsurgically from testis or epididymis
The purpose of IVF/ICSI treatment is to
- By pass the fallopian tube where fertilization normally occurs, so that tubal factor is overcomed
- By removing the oocyte, the quality of egg can be assessed
- Subtle hormonal defects get corrected and endometrial receptivity improves
- ICSI bypasses inherent weakness of fertilization of normal looking sperm like acrosome defet etc. It also overcomes failed fertilisation due to thick zona pellucida
In men with obstructive azoospermia (because of duct blockage or absence of the vas deferens), sperm are usually recovered from the epididymis by puncturing it with a fine needle. This procedure is called PESA (percutaneous epididymal sperm aspiration)
In TESA or testicular sperm aspiration (also known as TESE, or testicular sperm extraction), testicular tissue is sucked out through a fine needle, under local anaesthesia. The sperm are then liberated from tissue and used for ICSI.
Average success rate is around 30-35% but varies from case to case. Women with good ovarian reserve and PCOS have better cummulative success rates (60-70%) whereas women with poor ovarian reserve, damaged endometrium have poor success rate (20-30%).
- Success rate depends on
- Age of couple
- Pre IVF evaluation- use of OC pills, Use of estradiol valerate, use of leuprolide
- Stimulation protocol used
- Quality of gametes (eggs and sperms) & embryos
- Number of embryos transferred
- It starts on Day2 of menses. Baseline ultrasonography is done to rule of ovarian cysts. If required, baseline hormones like Serum E2, LH and P4 may be done to confirm that the ovaries are suppressed
- On basis of Age, BMI, Previous stimulation result, AFC and AMH , Injections are started
- Growth of follicle and endometrium is monitored by serial ultrasonography . Blood tests if required are done
- Dose of injections is increased, decreased or maintained, injections are added as and when required
- After 9 to 10 days of Injections , when 2 or more follicles are more than 18mm in diameter, trigger injection is planned
- 35 hours post trigger, oocyte pick up is done.Oocyte retrieval is a surgical procedure which is done under anaesthesia where the follicles are aspirated
- Aspirated follicles will be searched for oocytes, or eggs. Not every follicle will contain an oocyte
- All the oocytes which are retrieved are carefully identified and kept in the CO2 incubator
- Semen sample is obtained and semen processing done which isolates the healthiest sperms
- IVF/ICSI is performed in laboratory
- Formation of embryos and growth of embryos are monitored in the laboratory
- 3 to 5 days post fertilzation, embryo transfer is done. Embryo transfer is a simple procedure just like an IUI procedure done under sonography guidance. When the embryos are transferred on day 3, the embryo is said to be 8 cell stage. When the embryos are transferred on day 5, it is at the blastocyst stage. This is the highest form of human life that can be sustained in the laboratory
- If there are surplus good embryos , one can freeze them
- Luteal support is given
- Patient is asked to follow up after 15 days for result
- Treatment cycle can be cancelled if enough follicles don’t grow. It usually happens in older women and poor responders. It happens in around 5-6% of IVF treatment cycles.In such cases, different medications or protocols can be used in the next cycle
- Sometimes, inspite of follicles being formed, egg may not be there..that is empty follicle. It occurs due to improper trigger, ineffective trigger. It may require change in protocol and treatment regimen
- Embryo transfer may be postponed and all embryos frozen if there are excessive follicles that form like in PCOS
- There is an increased chance of multiple pregnancies and ectopic pregnancies due to the transfer of multiple embryos. However, the risks for pregnancy i.e. complications per se during pregnancy due to IVF treatment/ICSI & during delivery are unchanged
- Risk of birth defects after ICSI is the same as for babies conceived through IVF treatment without ICSI, and for those conceived naturally. However, in severe male factor infertility associated with balanced translocations and Y chromosome micro-deletion, transmission may occur to the male offspring
- It does not require bed rest or prolonged leave. It does not require over night admission
- Associated Endometriosis may affect the egg quality and implantaion
- Associated Fibroids, depending on size and location may need treatment
- Associated Hydrosalphix should be treated, as the fliud affects implantation and is embryotoxic
- Exercise and healthy diet help to fight oxidant stress and improve result
- Life cycle of sperm is approximately 3 months, hence the sperms that are expelled are produced 3 months prior.Hence use of alcohol, cigarette, tobacco should be avoided. Frequent ejaculation (every 2 to 3 days) should be recommend
- In some cases, pre cycle Hysteroscopy may be recommended
- In women with poor ovarian reserve, giving excessive injections doesn’t improve the outcome in terms of quantity and quality of eggs. It instead adds to cost and trauma to the patient
- Natural cycle IVF uses minimal or no drugs to recruit naturally selected follicle. It is extremely cost effective and provides a chance of conception to women with poor ovarian reserve
- Here rather than focusing on the quantity of the eggs the focus is on the quality of the egg collected
- The uterine lining is more receptive as there is minimal use of medication leading to better implantation
- Eggs can also be pooled using multiple cycles and then transferred back to the uterus
- The success rate of Natural Cycle IVF is reliant on a multiple factors that are beyond the control of the doctors. Therefore the success rates of Natural Cycle IVF are comparatively low as compared to Stimulated Cycle IVF fertility treatment
7. Treatment for Male Infertility.
Male infertility accounts for 50% of causes of Infertility.
When there are no sperms in the sample , it is called Azoospermia.
Azoospermia can be obstructive or non obstructive.
Obstructive azoospermia is due to block in the passage that the sperm has to travel. Ex -Absence of Vas deferens.
Non obstructive azoospermia is due to very low production or non production of sperms.
- Genital surgeries
- Undescended testis in adolescence
- Disease of genital tract
- Past history of Mumps
- Causes leading to increased heat in genitalia- Testis are placed outside the human body as they need lower than body temperatures to survive. Excessive heat can lead to damage to sperm production. Ex- Obese men (due to sagging layers of fat), truck drivers , tight underclothings, excessive sauna etc
- Smoking especially more than 20 cigarettes per day
- Excessive ejaculation- 2 to 3 times a day
- Genetic causes like CBAVD (Congenital bilateral absence of Vas Deferens) , Y chromosome microdeletion etc
- Treating Infections with antibiotics: Infections if present should be treated with the help of antibiotics .This is not always helpful Medications can be given to correct hormonal issues
- Correctable surgeries- Varicocele or an obstructed vas deferens may be repaired. In persistant oligospermia, IVF treatment offers good pregnancy results. To attain pregnancy via IVF treatment, even low sperm counts are sufficient
- In Azoospermia, sperm can often be retrieved directly from the testicles or epididymis using sperm retrieval techniques
- In PESA (percutaneous epididymal sperm aspiration), sperms are usually recovered from the epididymis by puncturing it with a fine needle
- In TESA or testicular sperm aspiration (also known as TESE, or testicular sperm extraction), testicular tissue is sucked out through a fine needle, under local anaesthesia. The sperm are then liberated from tissue and used for ICSI
- In case no sperms can be extracted through surgical procedure, semen sample from a matched donor can be used for IUI or ART treatment
Normally atleast 32% of the sample should show forward progressive motility.
Treatment options:
1) Lifestyle modification
- Reduce chemical exposure
- Improve diet
- Exercise regularly
- Take nutritional supplements- Antioxidants to reduce stress
- Stop Smoking, tobacco, alcohol, marijuana
- Stop using any anabolic steroids including any testosterone supplements
2) IUI (Intrauterine insemination)
- Intra-uterine insemination (IUI) also known as Artificial Insemination is a process in which the washed/processed semen is placed into the uterine cavity with the help of a catheter in and around the time of ovulation (release of egg from the ovary)
- The purpose of IUI treatment is to introduce the best and the most motile sperms high up in the uterine cavity i.e. as close to the ovum as possible so that the sperms have to travel the least distance
- Procedure and details are described separately
IVF with ICSI treatment has delivered most promising results in male infertilty.
Erectile and ejaculatory dysfunction require details history taking and counselling. At time, it can be corrected with the help of medications or use of vibrator.
If not correctable, Sperm sample can always be obtained by surgical procedures and ICSI treatment done to attain pregnancy.
8) Donor egg and Donor embryo treatment:
An embryo is formed with fertilization of an egg and a sperm .
In many conditions, like
- Advanced age
- Premature Ovarian failure or reproductive ageing
- Decreasing ovarian reserve
- Recurrent IVF failures due to poor oocyte quality
There is Risk of genetic disease transmission in offspring even with ART treatment, women’s eggs are not capable of forming a healthy embryo which can give rise to pregnancy.
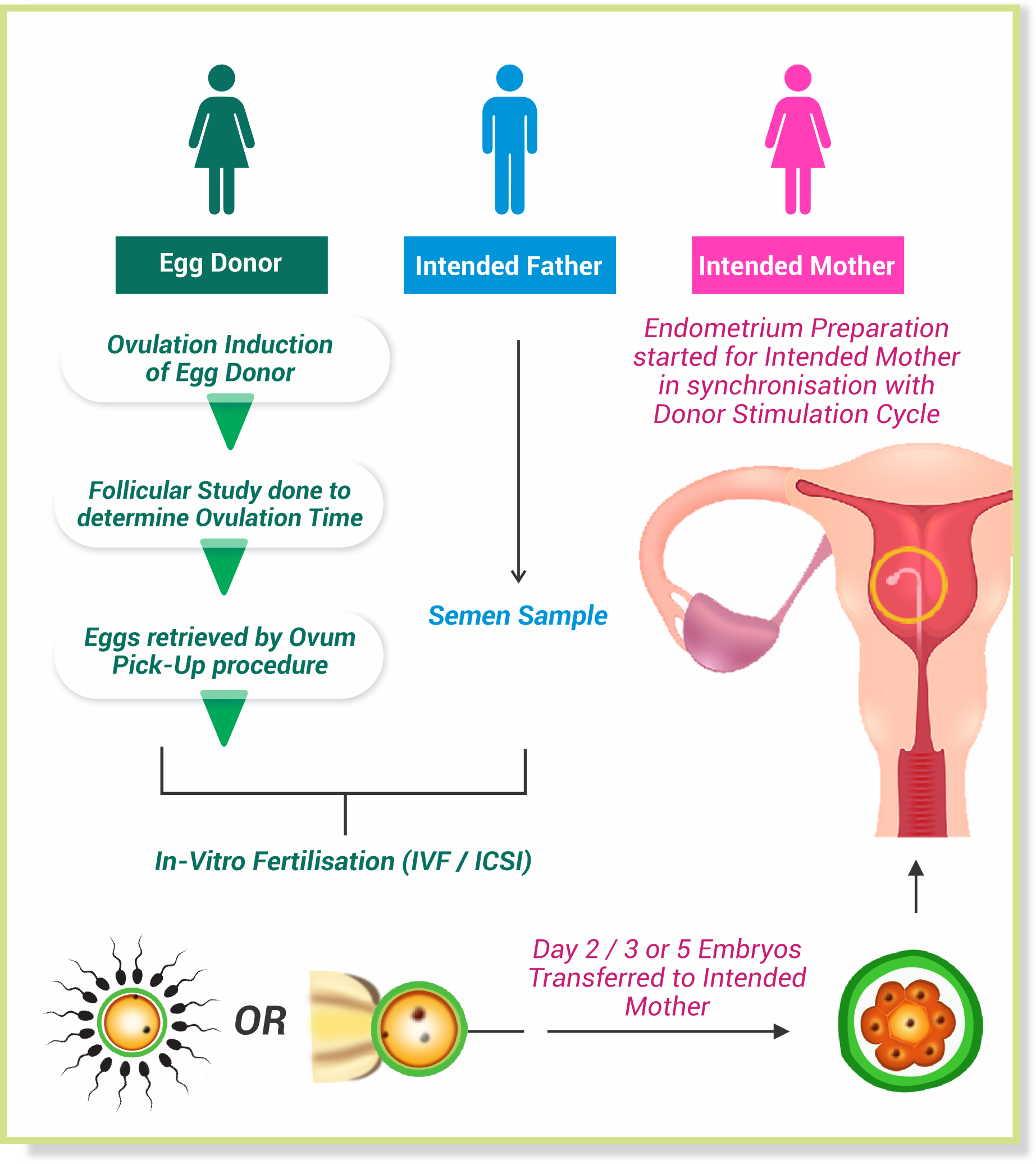
In such conditions, donor egg is one of the treatment option offered.
In this, Egg (Oocyte is obtained from young healthy donor)

Fertilized with Husbands sperm
 Donor egg Embryo is transferred in the female partner.
Donor egg Embryo is transferred in the female partner.
If above condition is associated with Azoospermia (sperms not retrieved surgically) or gentic abnormality in male partner, along with donor egg, donor sperm may also be used.
In this, Egg (Oocyte is obtained from young healthy donor)

Fertilized with Donor sperm

Donor Embryo is transferred in the female partner.
Young women of age group of 20-30
- Known fertility potential (Having their own genetically normal child within last 5 years)
- Not having any genetic disease or child affected with genetic disease
- No history of recurrent miscarriage
- No major medical or surgical illness
- No addiction
Detailed case history and examination of Donor is done
- Age/ Marital status/ Education/ Occupation
- Menstrual and Obstetric history
- Family history (history of any genetic/congenital abnormalities in any family member)
- Personal history(habits like using tobacco, smoking, drinking, what is the contraceptive being used)
- Detailed systemic examination done
Assement of her Ovarian Reserve
- Donor’s ovarian reserve is assessed with her blood AMH (Anti-Mullerian Hormone level) and her AFC count (Antral follicle count) seen on Ultrasonography.
Blood investigations to be done
- Routine tests- Hemogram and blood grouping
- Infection screening- HIV, HBsAg, VDRL, HCV
- Hormone profile- S.TSH
- Hb Electrophoresis
- Liver function test
- Renal function test
- Optional- Karyotyping
After matching the requirements, the donor is recruited.
- Matching with donor
- Synchronization of menses of donor and recipient
- Controlled ovarian hyperstimulation of donor
- Recipient’s treatment to prepare the endometrium for implantation Oocyte retrieval from the donor
- In vitro Fertilization of retrieved oocytes with the recipient’s husband’s sperm /Donor sperm obtained from Sperm bank
- Culture of embryos
- Embryo transfer in recipient’s uterus and luteal phase support
- Serum beta HCG level on day 14
As compared to the success rate of IVF with own eggs, success rates with donor egg and embryo are considerably high to the tune of 50-60%.
There are no problems associated with pregnancy after oocyte or embryo donation.
9) Oocyte , Semen And Embryo Freezing
- There are many couples or single individuals, who would wish to preserve their fertility potential (which decreases with age) and plan for family at a later stage
- This could be people with professional or personal reasons
- This could also be people unfortunately affected by cancer before finishing their reproductive life
- These individuals could opt for semen or egg freezing or the couple could opt for embryo freezing (embryo is formed using wife’s egg and husband’s sperm)
- These freezing facilities techniques provides time to the couples for accomplishing their desires and at the same time keeps the window of possibility open for them to become parents at a bit delayed stage of their life
